How is PAD treated
Lifestyle changes to lower your risk include:
- Stopping smoking (smokers are 4 times more likely to get PAD and have symptoms of PAD than nonsmokers.)
- Controlling diabetes
- Controlling blood pressure
- Being physically active (including a supervised exercise program)
- Eating a diet low in fat.
Drug treatment includes:
- Antiplatelet agents to prevent blood clots
- Cholesterol-lowering medicine (statins)
- High blood pressure medicine
Endovascular treatment includes:
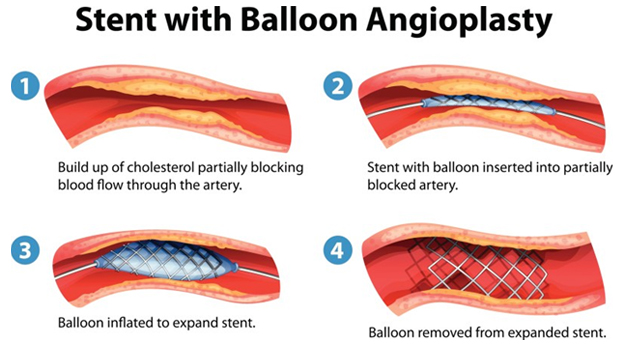
Angioplasty and Stenting: Angioplasty is a non-surgical procedure that widens narrowed or blocked arteries. A thin tube (catheter) with a deflated balloon on its tip is passed into the narrowed artery segment. Then the balloon is inflated. This pushes open the narrowed segment. Then the balloon is deflated and the catheter is withdrawn. Often a stent (a wire mesh tube) is placed in the narrowed artery with a catheter. There the stent expands and locks open. It stays in that spot, keeping the diseased artery open.
The Endovascular treatment generally takes few hours in a DSA suit with no scarring. Patients can usually resume normal activities the next day with minimal or no pain. The success rate of the Endovascular treatment is high and measurably better than the bypass or vascular surgery.