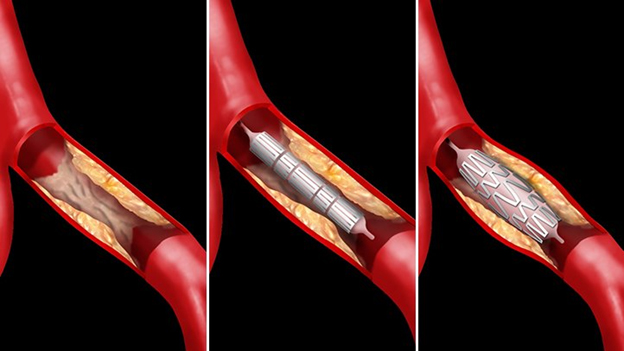
Stents used
Stenting used, Stents are small, strong expandable tubes made of metal mesh which when placed in the blood vessel support its walls from the inside
when is stenting used/ why use stent in addition to angioplasty
Stents are frequently used in conjunction with balloon angioplasty. The angioplasty part of the procedure opens the artery, however, if the narrowing cannot be extended sufficiently by means of a balloon dilatation, a stent can be placed into the vessel, to hold the artery open. Sometimes stents are used without prior angioplasty (this is usually because we have found that a stent will be needed in either the short or long term).
Over time, the artery wall heals around the stent. Another possible benefit of using a stent in addition to angioplasty is that it may decrease the number of procedural complications associated with just angioplasty alone. Sometimes drugs can be attached to stents (Drug Eluting stents) to try to reduce the longer-term risk of the artery narrowing where the stent has been placed.
Drug-eluting stents are frequently used in the heart (coronary stents), but are relatively infrequently used in the remainder of the body. This is because they have not been shown to be beneficial, are expensive and have a higher risk of some complications (such as sudden stent clotting and blockage).
How is stenting done/ is it a bigger producre
The stenting procedure is almost identical to the angioplasty procedure (mentioned above) with a short additional step of deploying the stent in the blood vessel. Initially, the stent is delivered on a small diameter delivery system to allow its access into the blood vessel. Once in position within the artery, it is expanded to fit the size, shape, and bend of the artery. The stent remains in the artery after the procedure to help keep the artery open. Within several weeks the artery wall grows into the stent which usually gets incorporated into the artery wall. In many cases, a balloon is still the first treatment step to stretch the artery open, however in some cases implanting a stent is performed without initial balloon dilatation first.
Following completion of the procedure, patients must then lie flat for a period of time. This can vary from hospital to hospital although is usually in the order of 4 hours. There will be some bruising around the catheter puncture site and it may feel a little sore as the anaesthetic wears off. Do ask the nurse for some painkilling tablets for this if it occurs. The doctor will discuss the results of the treatment with you before you go home. A letter will be sent to your General Practitioner explaining the details of the treatment.
what happens after angioplasty and stenting
Post Procedure Advice
Angioplasty or stenting will improve the blood flow in your artery but it will not cure the underlying cause of the blockage – arteries may become narrow again (called restenosis), which is why it is important to follow the advice below.
Any patient with this arterial disease, no matter which arteries are affected, stands to benefit from eating a low-fat diet, getting regular exercise, and controlling blood cholesterol.
Angioplasty improves artery blood flow for most people. But, results will depend on where your blockage was and how much blockage you may have in your other arteries. In many cases, you will be prescribed aspirin medication in an attempt to prevent the problem from occurring again and to reduce the risk of other artery related diseases such as heart attack and stroke.
If you are a smoker, it is very important that you stop smoking. Smoking causes the arteries to become narrowed and can also cause the blood to clot more rapidly.
The risk of progression or recurrence of disease of the arteries and its complications can be reduced after angioplasty and/or stent insertion by simple lifestyle modifications including:
- Weight reduction and exercise
- Eating a healthy diet, which is low in saturated fats
- Elimination of smoking
- Controlling high blood pressure, Diabetes mellitus and high cholesterol. Medications to reduce blood cholesterol (“statins”) are usually recommended and started by either the GP or the hospital doctors