About angioplasty
About Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat an artery which has become blocked or narrowed.
symptoms would I get from a narrow/ blocked vessel
Most of the blocked/ narrowed vessels we treat are in the arteries supplying the legs. As a result, the blood flow to the legs is reduced. This can cause pain in the legs, particularly when walking. In a more severe form there may be foot and leg pain at rest, and sometimes ulceration or even gangrene. Angioplasty is performed to relieve or improve these symptoms.
The procedure is performed in a hospital by an Interventional Radiologist (a doctor specially trained in minimally invasive procedures performed with the help of x-rays and other imaging technologies). The procedure is performed under sterile conditions. The skin will be cleaned and you will be covered with sterile drapes. A local anesthetic is used to numb the skin and then a small needle is put into an artery in the groin (usually).
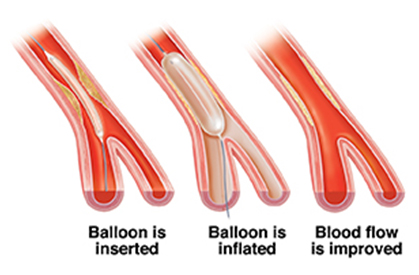
This needle is then exchanged for a small tube (catheter) which sits inside the artery and allows wires and tubes to be passed into the artery. The radiologist injects x-ray dye into the small tube and uses x-rays to identify the area where the artery is narrow or blocked. The radiologist then passes a thin wire through the narrow or blocked section of the artery. Another small tube with a deflated balloon on the end is passed over the wire. When the balloon is in the right place, it is inflated.
The balloon is then deflated and removed from the artery. More dye is injected to see if the narrowing or blockage has been successfully treated or if the balloon needs to be reinflated. The radiologist uses x-rays to see where the wires and tubes are throughout the procedure. Sometimes angioplasty is not successful and a wire mesh stent needs to be placed in the artery (see stent information).
At the end of the procedure, the small tube is removed from the groin and a doctor or nurse will need to press on the artery in the groin for around 5-10 minutes. This is to reduce the risk of bleeding and bruising. Sometimes a small device is used to help stop the bleeding more quickly.