Stroke is a disease that affects the arteries leading to and within the brain. It is the No. 5 cause of death and a leading cause of disability.
A stroke occurs when a blood vessel that carries oxygen and nutrients to the brain is either blocked by a clot or bursts (or ruptures). When that happens, part of the brain cannot get the blood (and oxygen) it needs, so it and brain cells die.
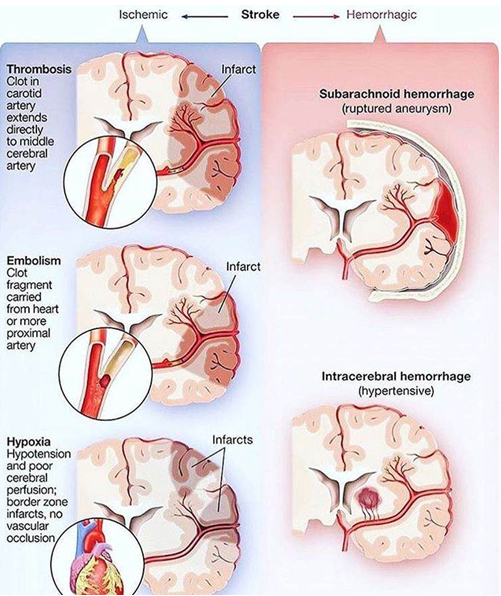
Stroke can be caused either by a clot obstructing the flow of blood to the brain (called an ischemic stroke) or by a blood vessel rupturing and preventing blood flow to the brain (called a hemorrhagic stroke). A TIA (transient ischemic attack), or “mini stroke”, is caused by a temporary clot.
The brain is an extremely complex organ that controls various body functions. If a stroke occurs and blood flow can’t reach the region that controls a particular body function that part of the body won’t work as it should.
As the ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes are caused by different factors, both require different forms of treatment. It is not only important that the type of stroke is diagnosed quickly to reduce the damage done to the brain, but also because treatment suitable for one kind of stroke can be harmful to someone who has had a different kind.
